Agile Leadership Development
for the new global economic world of
» relentless change
» ferocious competition
» unstoppable innovation
»»» rethink leadership for competition successes in the new global economic world!

Since the foundation of our company a good 20 years ago, our guiding principle has been "Corporate structure follows the corporate environments".
Even during the financial crisis of 2008/2009, the adjective "dynamic", which in the economic comfort zones of the world such as Germany, Austria, Switzerland until 2020 was gladly only noted.
Since the beginning of 2020, the adjective "dynamic" has received special attention.
Like a burning glass, first the corona pandemic then the war in Ukraine affected all subsystems of society (see picture above) and thereby upset the individual subsystems in society, as if an invisible particle accelerator were in use worldwide.
Did it take more drastic impulses from the outside - the environments - for real changes to take place inside?
Apparently, yes!
In order to get a place in the new world economic order, the changes are vital for survival.
For sustainable success in dynamic markets, management is not about making the wrong thing faster inside the company.
It is a question of the company organization with its
- Management, business and support processes as well as
- Projects
to become a successful player in global business ecosystems.
> You don´t establish an agile organization forcing company employees to hold hands and sing Kumbaya around the kicker table.
>> We need to rethink management to build agile organizations that can operate successfully in the new global economic order that is currently emerging!
Our Services
- Create company-specific strategies for candidate scouting/promotion/development
- Define the agile manager profiles for the company's value ecosystem and the required future competencies
- Introduce scouting internally and externally to the company to find potential agile managers
- Select the most suitable candidates
- Select talented individuals within the company to promote and develop the agile talents, prepare them for their task
- Tap the potential of talents through future-oriented development measures, develop them
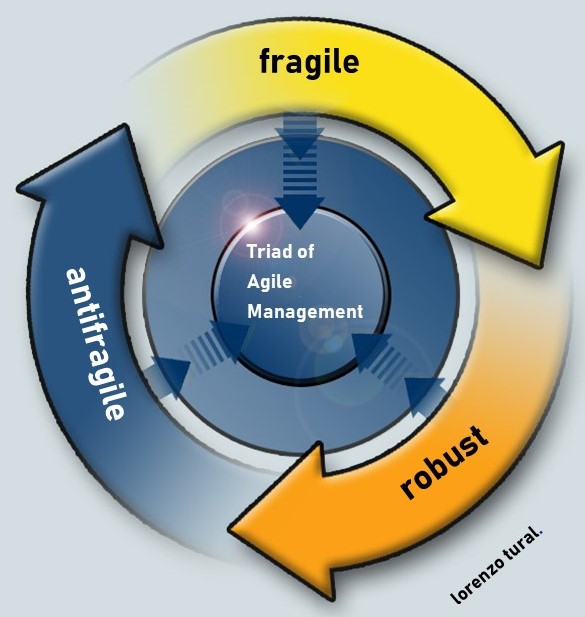
» Fragile organizations, which are immediately unable to cope with a shock.They avoid the mess and are susceptibile to disorder.
» Brittle organizations, which carry on for a while but ultimately fail.
» Resilient organizations, which experience a dip resulting from the shock but which ultimately return to the same level of performance as before.
» Antifragile organizations, which not only survive a shock, but become stronger through it.They gain from Disorder.
In the organizational map of companies there are all four types of organizations.
Leadership Challenge in the new global economic system is to steer the company towards the entrepreneurial purpose with such a map.
The work of an agile organization does not stop when the world rebalances after the Corona pandemic and the Ukraine war.
Rather, it is the trigger after which the organization begins to think about its next phase of transformation and growth.
By leveraging lessons and insights from the current period, a resilient organization can accelerate its transformation and shed the pre-pandemic inertia that previously prevented the organization from achieving its transformation goals.
For the problem-solving design of agile organizations, we are guided by a model -based on Payoff Matrix (Game Theory)- with two different types of decisions and two different classes of contingencies.
In practice, several approaches exist for applying Payoff Matrix. We have chosen the Talebs approach and think it further for the design of agile organizations.
Two distinct classes of probability structures:
There are two classes of probability domains—very distinct qualitatively and quantitatively.
The first, thin-tailed: Mediocristan, the second, thick tailed Extremistan.
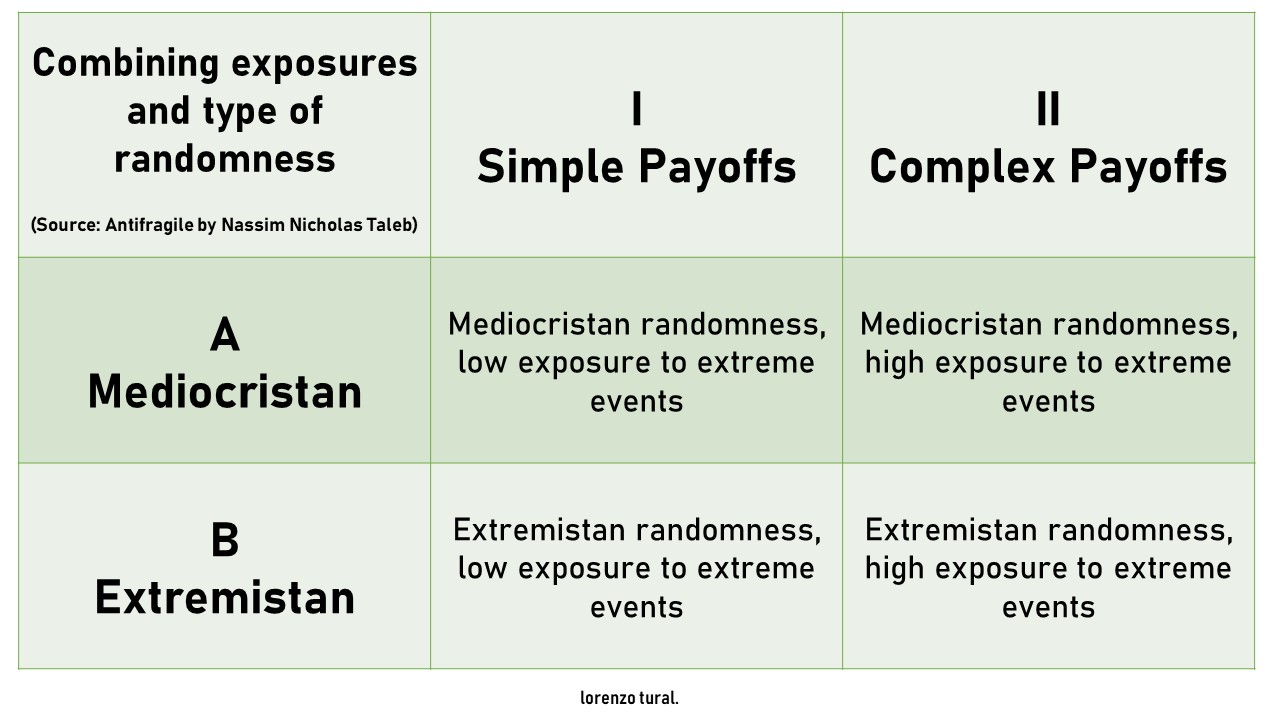
Skills, terms, techniques, theories, methods, tools are suitable for each type
»» fragile,
»» brittle,
»» resilient,
»» antifragile"
and for each quadrant
»» Mediocristan & Simple Payoffs
»» Mediocristan & Complex Payoffs
»» Extremistan & Simple Payoffs
»» Extremistan & Complex Payoffs
» How to introduce them?
Two distinct types of decisions:
The first type of decisions is simple, "binary", i.e. you just care if something is true or false.
Very true or very false does not matter. Someone is either pregnant or not pregnant.
A statement is "true" or "false" with some confidence interval. (we call these M0 as, more technically, they depend on the zeroth moment, namely just on probability of events, and not their magnitude —you just care about "raw" probability).
A biological experiment in the laboratory or a bet with a friend about the outcome of a soccer game belong to this category.
The second type of decisions is more complex.
You do not just care of the frequency—but of the impact as well, or, even more complex, some function of the impact.
So there is another layer of uncertainty of impact. (we call these M1+, as they depend on higher moments of the distribution).
When you invest you do not care how many times you make or lose, you care about the expectation: how many times you make or lose times the amount made or lost.
The Leadership Map in the new global economy
Mediocristan is a process dominated by the mediocre, with few extreme successes or failures.
No single observation can meaningfully affect the aggregate.
Also called “thin-tailed” or member of the Gaussian family of distributions
Extremistan is province where the total can be conceivably impacted by a single observation.
Also called “fat-tailed”. Includes the fractal, or power-law family of distributions
First Quadrant:
Simple binary decisions, in Mediocristan: Statistics does wonders.
These situations are, unfortunately, more common in academia, laboratories, and games than real life—what I call the "ludic fallacy".
In other words, these are the situations in casinos, games, dice, and we tend to study them because we are successful in modeling them.
Second Quadrant:
Simple decisions, in Extremistan: some well known problem studied in the literature.
Except of course that there are not many simple decisions in Extremistan.
Third Quadrant:
Complex decisions in Mediocristan: Statistical methods work surprisingly well.
Fourth Quadrant:
Complex decisions in Extremistan: Welcome to the Black Swan domain. Here is where your limits are.
Do not base your decisions on statistically based claims. Or, alternatively, try to move your exposure type to make it third-quadrant style ("clipping tails").

Have you already described the dynamics in the environment of your company or your project?
Don´t forget: even what you can't measure, you have to be able to manage!
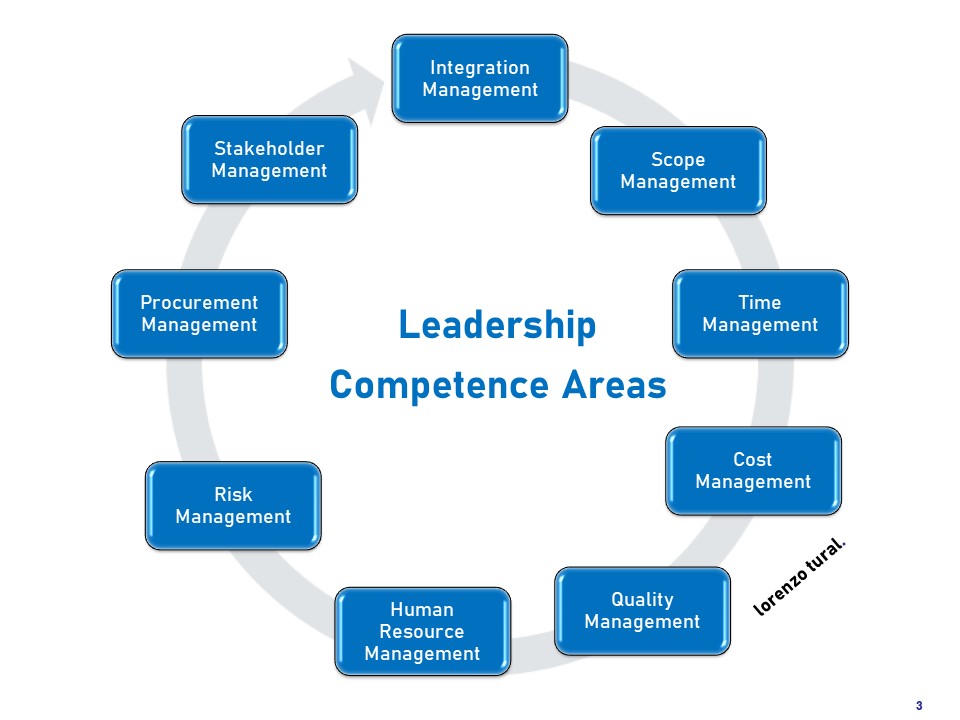
9 Leadership Competence Areas >>> we need to rethink it in terms of agility
+49 (0)1590 1497679
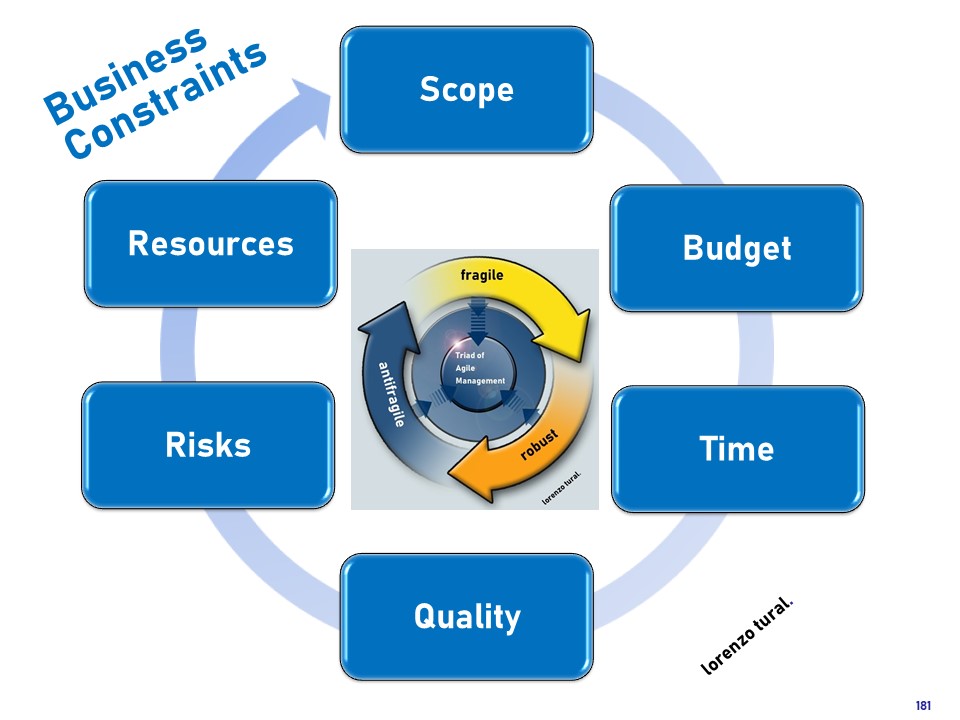
The Impact of 6 Business Constraints on the Triad of Agile Management
>>> more about Agile Management ...